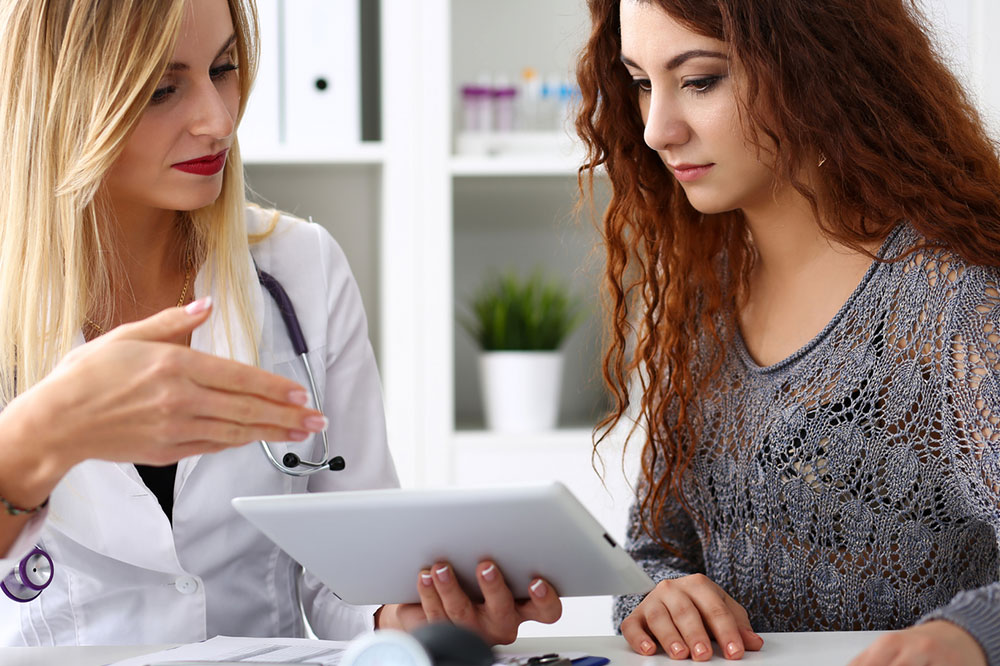
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be both acute and chronic. If the infection has been present for a while, it is a chronic infection. However, the sad part about chronic hepatitis C is that it remains silent for years, and later when the virus has badly affected the liver, symptoms start showing. Here, we’ll discuss some common signs and diagnosis of hepatitis C.
Symptoms
Some of the key symptoms of hepatitis C include:
- Easy bruising
- Easy bleeding
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice
- Itchiness in the skin
- Urine is dark-colored
- Ascites, which is a build-up of fluid inside the abdomen
- Incomprehensible weight loss
- Swelling on the limbs, mainly legs
- Drowsiness
- Slurred speech
- Spider angiomas
- Confusion
In hepatitis C, it is important to note that the virus usually starts with the acute phase. However, since it does not depict any significant symptoms, it goes undiagnosed. However, when the symptoms appear in the early stages, they are common signs of the disease.
Some symptoms in acute stages of hepatitis C include:
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Fever
You will not experience symptoms in the acute stages immediately. It only appears in a few weeks or months after you have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
Diagnosis
The signs and diagnosis of hepatitis C are co-related. When you experience any of the above-listed symptoms, you should reach out to your healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. The doctor will perform various tests before confirming if it is hepatitis C. These include:
Blood tests
In case, in the initial blood tests, there’s a sign of the presence of hepatitis C infection, the doctor will perform additional tests for confirmation. These will be done to:
- Examine the degree of the virus in the blood
- Identify the virus’ genotype
Liver damage examination tests
After blood tests, the doctor will perform a liver examination test to determine the liver’s damage as a result of the hepatitis C. These tests will be performed:
- MRE
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) is non-invasive and is a preferred alternative to liver biopsy. Under this, MRE and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) technologies are combined. This leads to the formation of patterns by the sound waves produced as a result of them bouncing off around the liver. As a result of this, a visual image is deduced that showcases the liver’s degree of stiffness. If the liver is stiff, it could be a sign of liver fibrosis, a common symptom of hepatitis C in the chronic stage. - Liver biopsy
In this test, a slim needle is inserted via the abdomen to the liver to acquire a liver tissue sample. This sample then undergoes lab testing for further diagnosis. - Transient elastography
Again, a non-invasive method under which vibrations are transmitted in the liver to measure the dispersal speed. This is also done to determine the stiffness in the liver.
- Blood tests to determine the severity of liver fibrosis
Different blood tests are performed to analyze the spread of liver fibrosis.